To improve the quality and function of plastic products
Technology lecture for FIM/IMD 2nd session: Explanation of the screen printing process.

In our last White Paper we talked about Film Insert Molding & In-Mold Decoration, which is the major technology of plastic molding products that expands the market armed with metal substitution, weight reduction, and cost reduction.
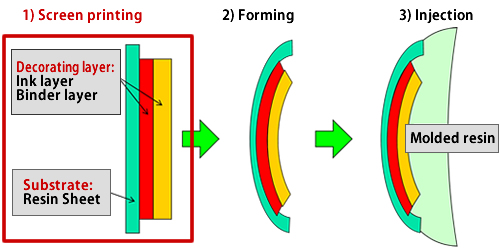
Our objective in the White Paper is to describe and explain "Screen printing", which is the first process stage in the 3 process stages of this Film Insert molding (FIM/IMD).

1. First process stage of FIM/IMD: Screen printing
Screen printing is a kind of stencil printing and is regarded as a general term of “Printing technique by stretching the screen fabric made of synthetic fiber or stainless-steel line, etc. on a frame and filling mesh by using gelatin or resin except for printing area (for photopolymerization) and extruding ink through exposed texture.”
In FIM/IMD, print is to be made on the film which is processed in the forming and injection process later. Also, the binder, etc. are used as needed.
Characteristics of screen printing
=> It is possible to provide thicker thickness of the printed ink layer (3µm – 400µm) – => It becomes easy to obtain resistance of printed surface.
=> Screen print can be undertaken on a wide variety of substrates which allows of a wide choice in form, size, and strength of substrates, and even includes the capability of printing on 3D objects.
2. Functions that the screen printing process can enable
Molding ink used in FIM/IMD is available as 1 pack type ISX-HF, 2 pack type IPX-HF and INQ-HF, and a Binder-IMB-HF for 2 pack type ink.
Functions that screen ink can enable
The above FIM/IMD ink makes it possible to provide various functions in addition to the function necessary for molding. This enhanced functionality allows FIM/IMD to add various value to the products that paint or metal plating can not realize.
This is a list of some of the functions enabled by our FIM/IMD inks:
- Selective wavelength transmittance (IR transmittance function, etc.)
- Phosphorescence
- Mirror Ink Metallic finish (mirror effect ink)
- Jet-black finish that simulating lacquer (Piano Black)
- Others (Non-conductivity, antibacterial, etc.)
Example of the IR transmittance function (This photo illustrates visual ray transmittance.)

Example of phosphorescent function (The photo illustrates N luminous phosphorescence.)

In our next White Paper, we will explain about forming process and introduce the relevant inks.
So we hope you will enjoy our next White Paper, No. 3 in our FIM/IMD series.
Please also refer to detailed information about molding inks referred to in this White Paper as follows.
| ISX-HF | 1 pack type | High elongation property. Good workability with no pot life. |
|---|---|---|
| IPX-HF | 2 pack type | Wash out resistance, high resistance of ink surface, heat resistance in forming and molding |
| INQ-HF | 2 pack type | Flexibility and high resistance of ink surface in forming |
| IMB-HF006 IMB-HF009 |
1 pack type | Binder ink (Adhesive layer between molded resin and ink surface)(Use when using IPX-HF, INQ-HF.) |
- Related technology information
- Related event information

